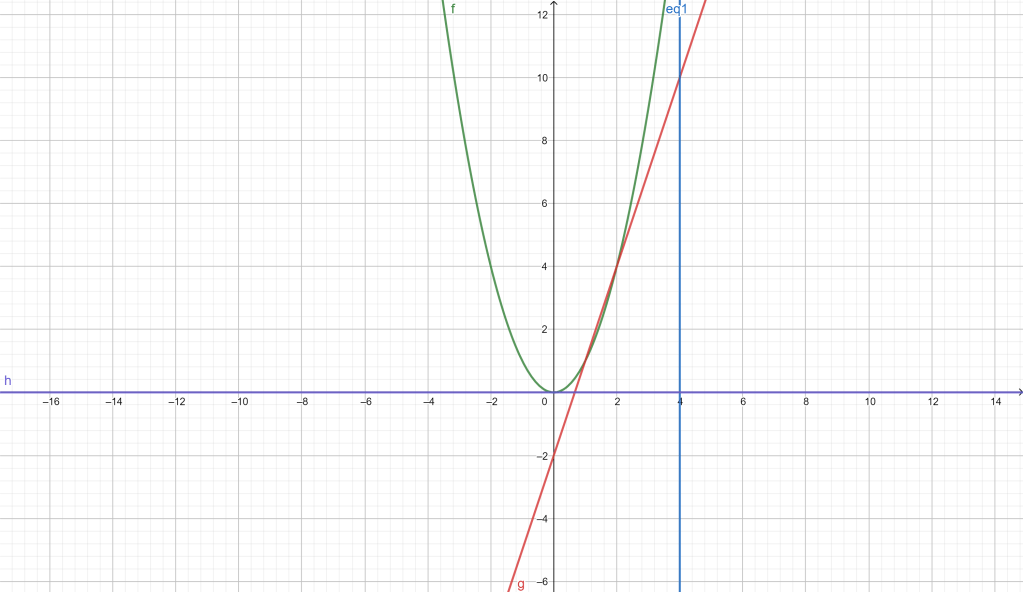
First, graph the quadratic polynomial, here I have graphed x^2.
Next, draw a vertical line to touch the tip of the curve, although this image does not show it touching the curve it does in fact do so, here I graphed x=4 for the vertical line
Now, draw a horizontal line that is equal to zero.
Next, find a tangent line for the curve, I picked 3x-2 as the tangent line,Evaluate the straight line’s gradient e.g find its derivative using y2-y1/x2-x1. This tangent line was found via trial and error but if you want a more accurate tangent line use the distance between two points formula at 0,0 for this case and then at the tip of the curve. The following link is attached if you don’t know or understand what it is.
https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/distance-2-points.htmlFinally, to integrate where both the straight line and the vertical line is the triangle you want to integrate, find the length of the height of the triangle and the length of the base of the triangle, now find the area using base times height divided by two.
Now we have successfully differentiated and integrated the quadratic polynomial presented to us. By the way, this is my own method of evaluation, feel free to use it but please do attribute it to me or my blog. Down below is how it should look.
https://www.geogebra.org/graphing
Thank you for reading this,
Nunghead